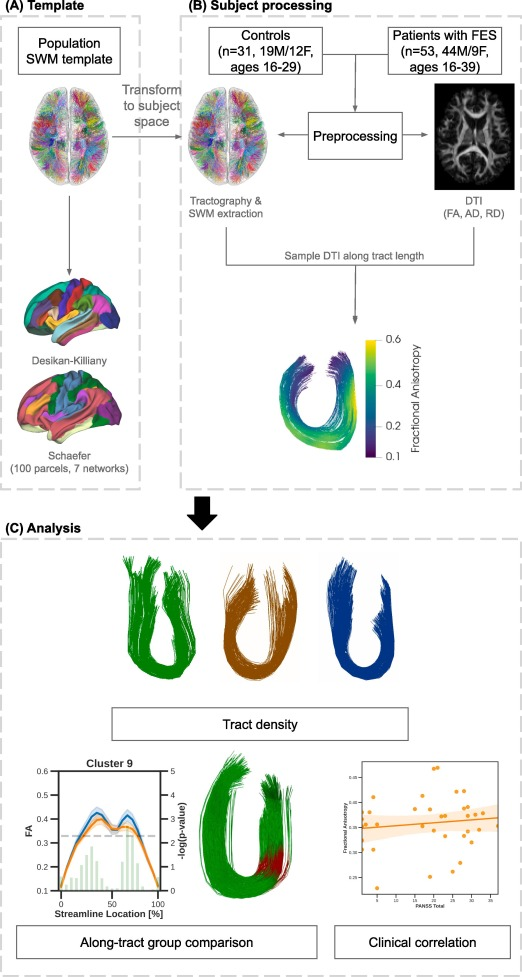
White matter bundles provide the beams and bridges that connect various parts of our brain.
A special type of white matter is the one immediately below the surface of our brain. These structures, called ‘U’ fibers, are a group of short association fibers that connect adjacent gyri (folds) within the same hemisphere of the brain. They are bent in a a U-shaped loop that allows them to run ‘under’ the sulci (valleys).
They are not as well studied as other types of cortical fibers. But they are thought to play a role in forming and maintaining the ridges and folds that form the cortical structure, and a range of cognitive functions. These bent bridges are likely responsible for communication between nearby cortical areas, especially in association cortex (e.g., frontal lobe).
We studied the integrity of these ‘U’ fibers in the frontal cortex in very early stages of schizophrenia. We note very small amount of changes at this early stage of illness. the fact that these fibers remain mostly unaffected is indeed a good news for patients in early phases of psychosis.
This work was led by Dr. Jason Kai for his doctoral work supervised by Dr. Ali Khan, our collaborator. You can read the open access paper here.